It is often confusing to understand Google’s policies when it comes to content to be removed from Google search results including Google Image Search Engine. Accordingly, I’m creating new tutorials for getting rid of content that appears through Google (or Google services).
First, to be able to remove personal photo or image that is hosted on third-party website, you must initiate contact with the website owner where the image is at and get them to delete the image. If the website owner is not responsive or doesn’t delete the photo, then, you may consider contacting the web hosting company because that image is stored on their web server.
Second: before making a claim, ask this
- Is the photo/image published on external website against Google image publishing guidelines (including SafeSearch)?
- Does the particular image/photo fall within content removal policies Google abides by
This is important to understand before making a removal request, or else, Google will not remove the image. Also, your future attempts will be affected by your previous claims.
EU Citizens Only
If you are citizen of an European Union country, then, you are in a better position because European data protection laws protects you differently. You can use “Right to be forgotten” for removing an image or a photo of yourself (or your child).
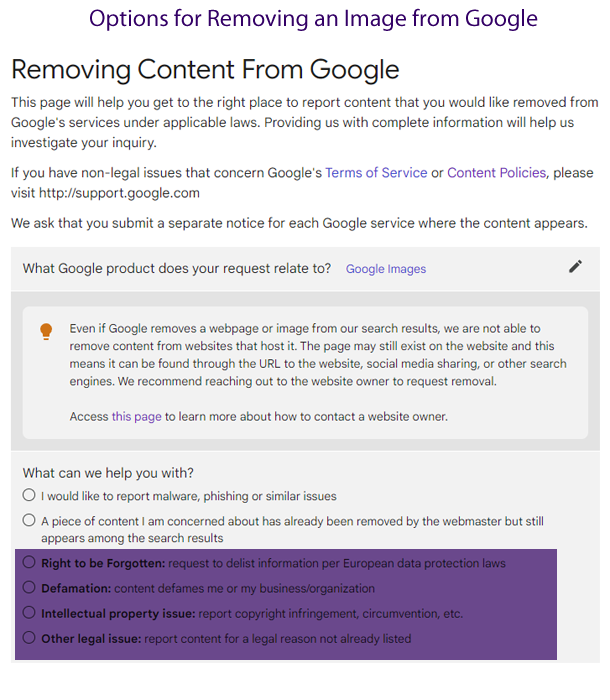
Options for Removing Content From Google
As far as Google is concerned ‘Content’ means anything digital including an image (any format including gif, png, jpg, webp, EPS, AI, PDF or others) which Google has the ability to index.
Under applicable laws of your country of citizenship, a person can report content that they would like Google to remove from its search and services. This page highlights your options for content removal policies and procedures.
RankYa’s Suggestions for The Options for Removing an Image
- I would like to report malware, phishing or similar issues (this is for concerned citizens only and doesn’t really apply for most people losing sleep over an online image or photo of themselves)
- A piece of content I am concerned about has already been removed by the webmaster but still appears among the search results (you can ignore this because Google will delete that image next time it visits that external website)
- Right to be Forgotten: request to delist information per European data protection laws (EU citizens use this)
- Defamation: content defames me or my business/organization (this covers a wide spectrum of legal definitions, this can be used for past criminal convictions, mugshot image, damaging information about a person and or business etc.)
- Intellectual property issue: report copyright infringement, circumvention, etc. (if all else fails there is a technique one can consider, and that is by quickly creating a website, publishing the same image, then, changing the date/time of publication to be earlier so that one can then claim copyright over the image you want removed. This may be ideal is rare cases when all else fails and Google does not remove the image.
- Other legal issue: report content for a legal reason not already listed (this covers a wide scope, it could be anything related to particular laws of a country and your legal rights under that law)
Part 1 Video for Removing an Image from Google Search
Part 2 Video for Removing an Image from Google for Legal Reasons
Tips for Dealing with Google
Understand that Google is a global multilingual search engine, although founded in USA, they now operate throughout the world and have different policies according to the country in which they operate to provide their products and services.
How is that important for you to know? Depending on the country you are a citizen of, certain laws protect you differently. For example: EU Citizens can use Right to be Forgotten but Australian Citizens can not use this option. Furthermore: US Citizens and their judicial system may require a Courty Order to be sent, whereas in Australia, our Defamation laws a bit different
In Australia’s Legal system, defamation means causing serious harm to a person’s reputation by publishing material about them that changes the way people feel about them. Not-for-profits and small businesses with fewer than 10 staff can also sue for defamation. Publishing includes speaking, writing, drawing, photographing or blogging.
Once again, do NOT make a claim or report a legal removal issue first before thoroughly understanding Google policies and guidelines.
When All Else Fails?
You’ve contacted the website owner, or web hosting company, you’ve read Google’s policies and used the web form and submitted a removal request to Google. You’ve hired a lawyer and followed legal avenues, or hired so called Google experts and reputation management services, and yet, nothing worked and that image or a photo still exists online available on Google. It is not end of the world because that image lives in a digital space.
If in your heart of hearts you believe it is wrong and unfair that someone has published an image about you (or your child) and you do not want anyone to see online. And no one is able to help you remove that content, then, here are other options.
- You can find the person (or persons) responsible for the website where the image is published. Then, counteract information which they themselves find unpleasant.
- Bury Google results for a particular name or image
- Confuse Google algorithms as to what keywords it should show for a particular search term
- You can make copyright claim
- Create positive content according to the name searched
- Create confusing content according to the keywords searched. For example: when someone searches for a particular Name Keyword, cute cat image shows up OR someone historical figure shows up confusing the internet surfer (including Google)


